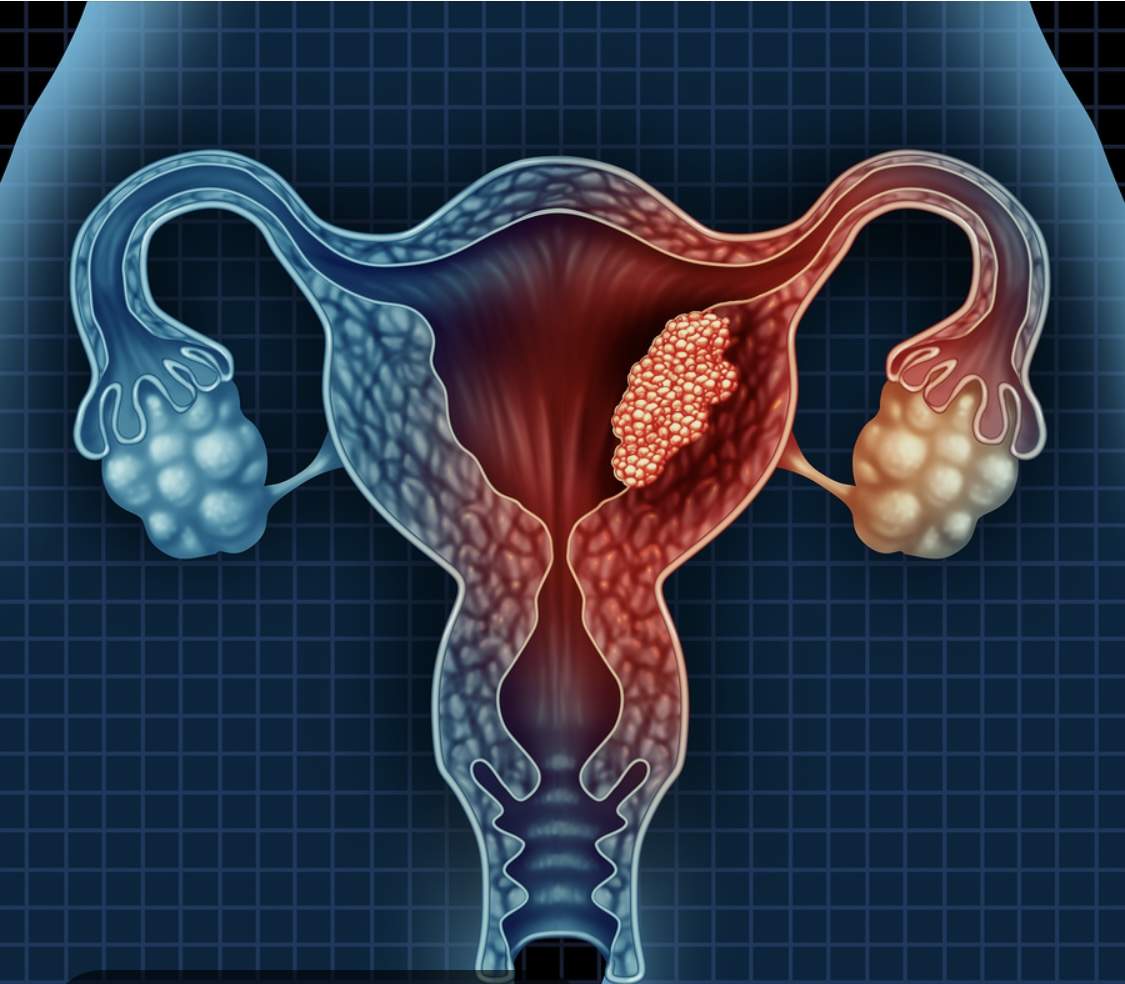
Non-cancerous growths that form in or around the uterus are called fibroids, sometimes referred to as myomas or uterine fibroids. The size of these growths, which are composed of fibrous tissue and muscle, ranges from pea-sized to melon-sized.
Since fibroids frequently don’t cause any symptoms, many women are unaware that they have them, even though they are common—up to 70–80% of women by the age of 50 may have them.
What Are Fibroids?
Fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) tumours that form in the muscular wall of the uterus. The exact cause of fibroids is still not fully understood, but researchers believe that they are linked to hormonal changes, particularly the influence of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones stimulate the growth of fibroids, which is why they are most often found in women of reproductive age.
Fibroids can grow in different areas of the uterus and are classified by their location, In subsequent articles we will discuss more of the types of fibroids.
Common Symptoms of Fibroids
Heavy menstrual bleeding: Women with fibroids may experience unusually heavy periods or prolonged menstrual cycles.
Pelvic pain or pressure: Depending on the size and location of the fibroids, they can cause discomfort or a feeling of pressure in the pelvic area.
Frequent urination: Fibroids that press against the bladder can cause frequent urination or difficulty emptying the bladder.
Pain during intercourse: In some cases, fibroids can make sexual activity painful.
Back or leg pain: Larger fibroids may put pressure on surrounding structures, leading to discomfort in the back or legs.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of fibroids is unclear, several factors may contribute to their development, including:
Hormones: Estrogen and progesterone play a significant role in fibroid growth. These hormones stimulate the development of fibroid cells during a woman’s reproductive years.
Genetics: Women with a family history of fibroids are more likely to develop them.
Age: Fibroids are more common as women age, especially during the reproductive years.
Ethnicity: African-American women are more likely to develop fibroids at a younger age and may experience more severe symptoms compared to women of other ethnicities.
Obesity: Overweight women are at a higher risk of developing fibroids, possibly due to higher estrogen levels associated with excess body fat.
Diet: Some studies suggest that a diet high in red meat and low in green vegetables may increase the risk of fibroids.
Many women suffer from fibroids, a common ailment that can bring discomfort and difficulties, but there are several treatment options available. Regular check-ups with your doctor are essential to monitor your health and address any concerns early on, regardless of whether you suffer symptoms. The majority of women with fibroids lead happy, healthy lives when their condition is properly managed.
Read Also-Promoting Healthier Lives: The Vital Role of Exclusive Breastfeeding